As AI becomes increasingly embedded in workplace tools, questions of data protection, privacy, and trust have never been more critical.
Microsoft Copilot, integrated into Microsoft 365 and enterprise platforms, promises major productivity gains—but is it secure?
Is Microsoft Copilot Secure?
Yes, Microsoft Copilot is designed from the ground up with security and compliance in mind. It operates within a multi-layered, defense-in-depth security framework that includes:
- Secure engineering practices aligned with Microsoft’s Security Development Lifecycle (SDL)
- Threat intelligence and AI-specific protections such as real-time classifier-based prompt injection detection
- Data access strictly controlled by Microsoft Entra ID permissions, sensitivity labels, Conditional Access policies, and Microsoft Purview data governance
- Strong compliance alignment with GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, FedRAMP, and the EU AI Act, among others
Copilot only accesses data users are authorized to view within their Microsoft 365 tenant, ensuring that sensitive information never leaks outside these boundaries. Microsoft also enforces encryption, data isolation, and containment strategies to prevent data exfiltration or unauthorized use.
Is Copilot Safer Than ChatGPT?
For enterprise environments, yes—Copilot offers stronger security and governance controls tailored for business data compared to the general public ChatGPT models.
Key differences include:
| Feature | Microsoft Copilot | ChatGPT |
| Data Governance | Enforces enterprise-wide policies via Microsoft Purview, Entra ID, DLP, and Zero Trust frameworks | Limited governance; user data may be used for training unless explicitly opted out |
| Integration | Embedded natively in Microsoft 365 apps with tenant-scoped access | Standalone platform without native enterprise integration |
| Security Controls | Multi-layered defenses including prompt injection protection, environment sandboxing, and encryption | Basic protections; more vulnerable to misuse and adversarial attacks |
| Compliance | Meets GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, HIPAA, FedRAMP, EU AI Act, and more | Not designed for enterprise-grade compliance by default |
| Governance Tools | Supports lifecycle management, automated data classification, and auditing | No built-in enterprise governance framework |
Unlike ChatGPT, Microsoft does not use Copilot customer data to train its large language models. Customer data accessed by Copilot remains private to the organization, aligned with Microsoft’s data privacy policies.
You may also like: Free ebook: Transforming your enterprise with Microsoft 365 Copilot
Are There Security Risks with Copilot?
While Microsoft Copilot is built with robust security, as with any advanced technology, risks exist:
- Over-permissioned Access: If user permissions in Microsoft 365 are too broad, Copilot can surface data those users can access, raising exposure risk
- Prompt Injection Attacks: Microsoft continually mitigates risks through advanced classifiers, filtering, and runtime session controls to block malicious inputs
- Data Leakage: Encryption, tenant isolation, and containment limit exposure or exfiltration of data
With diligent governance, adherence to least-privilege access, and sensitive data labeling, these risks are manageable.
You may also like: Microsoft 365 Copilot Prerequisites: What You Need to Know
Can Enterprises Trust Copilot?
Enterprises can trust Copilot as much as they trust their existing Microsoft 365 security posture.
Copilot respects all tenant boundaries and data governance policies configured by administrators. Microsoft’s internal Copilot deployment stresses sensitivity labeling, lifecycle controls, and user attestation to maintain data trustworthiness.
You may also like: Microsoft Copilot Implementation Plan: The First 10 Steps
5 Copilot Security Best Practices You Can’t Ignore (With Real-World Case Studies)
1. Implement Zero Trust Architecture
What Zero Trust Means for Copilot:
Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” treating every connection and resource request as potentially hostile. For Copilot deployments, this means implementing comprehensive verification at every layer.
Essential Components to Deploy:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Conditional Access:
- Configure risk-based authentication through Microsoft Entra ID
- Set up device compliance requirements using Microsoft Intune
- Implement location-based access controls for sensitive data
- Establish session controls that evaluate user behavior in real-time
Least Privilege Access Principles:
- Conduct Just-In-Time (JIT) and Just-Enough-Access (JEA) reviews
- Implement role-based access controls aligned with job functions
- Regular access reviews to eliminate permission bloat
- Automated access provisioning and deprovisioning workflows
Device Management and Compliance:
- Enforce device enrollment in Microsoft Intune
- Require compliant devices for Copilot access
- Implement app protection policies to prevent data leakage
- Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for threat detection
Threat Detection and Response:
- Deploy Microsoft Defender XDR for comprehensive threat monitoring
- Configure automated threat response workflows
- Implement user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA)
- Enable real-time security alerts and incident response
Case Study: Microsoft’s Internal Deployment
Microsoft applied Zero Trust principles across its 300,000+ employee Copilot rollout. The implementation included:
- Mandatory MFA for all Copilot access
- Device compliance verification through Intune
- Conditional Access policies based on user risk scores
- Real-time threat monitoring with Defender XDR
Results: Zero security incidents during rollout, 99.9% authentication success rate, and full compliance with internal security policies.
🔗 Apply principles of Zero Trust to Microsoft 365 Copilot
2. Use Sensitivity Labels and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies
Comprehensive Data Classification Strategy:
Sensitivity Label Implementation:
- Create a taxonomy covering all data types: Highly Confidential, Confidential, Internal, Public, Personal
- Apply automatic labeling based on content analysis and machine learning
- Configure visual markings (headers, footers, watermarks) for classified content
- Set up encryption and access restrictions tied to label classifications
- Enable cross-platform labeling across Microsoft 365, Azure, and third-party apps
Advanced DLP Policy Configuration:
- Block Copilot processing of highly sensitive data using the Microsoft 365 Copilot policy location
- Configure policies to prevent data exfiltration through prompts and responses
- Implement content inspection for financial data, PII, and regulatory information
- Set up policy tips to educate users about data handling requirements
- Enable advanced classifiers for industry-specific sensitive information types
Auto-Labeling and Machine Learning:
- Deploy trainable classifiers for organization-specific content types
- Configure auto-labeling policies for emails, documents, and SharePoint sites
- Implement exact data match (EDM) for highly sensitive structured data
- Use named entity recognition for automatic PII detection
Testing and Validation:
- Establish sandbox environments for policy testing
- Conduct regular policy effectiveness reviews
- Monitor false positive rates and adjust sensitivity thresholds
- Validate cross-application label consistency
Microsoft Modeling : Contoso’s GDPR Compliance Implementation
Contoso Corporation implements comprehensive sensitivity labeling and DLP for their Copilot deployment:
Implementation Details:
- Create a five-tier classification system aligned with GDPR requirements
- Deploy auto-labeling for 2.5 million documents within 30 days
- Configure DLP policies to exclude “Personal” and “Highly Confidential” data from Copilot summaries
- Establish 24/7 monitoring for policy violations
Modeling Results:
- 99.2% automatic classification accuracy
- Zero GDPR compliance violations
- 85% reduction in manual classification efforts
- Full audit trail for regulatory compliance
The implementation ensured that while employees benefited from AI productivity gains, sensitive personal data remained protected from Copilot processing, meeting stringent GDPR requirements.
🔗 Explore the DLP configuration
3. Audit Permissions and Oversharing
Comprehensive Permission Auditing Framework:
SharePoint and Teams Security Reviews:
- Conduct quarterly reviews of sharing settings across all SharePoint sites
- Analyze external sharing permissions and guest access patterns
- Implement restricted SharePoint search to limit Copilot data access
- Review Teams channel permissions and membership hierarchies
- Audit shared mailbox and distribution list permissions
Microsoft Entra Access Management:
- Deploy access reviews for all security groups and distribution lists
- Implement automated workflows for privilege escalation requests
- Review service principal permissions and application registrations
- Monitor privileged role assignments and administrative access
- Establish regular recertification processes for high-privilege accounts
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities:
- Use Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps for real-time activity monitoring
- Deploy Microsoft Purview compliance solutions for data governance
- Implement Azure Monitor for custom security analytics
- Configure Power BI dashboards for permission and access reporting
- Establish automated alerting for suspicious access patterns
Oversharing Detection and Remediation:
- Deploy Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention for oversharing detection
- Use Microsoft 365 Compliance Center for content exploration
- Implement automated workflows for permission right-sizing
- Configure sensitivity-based access controls
- Establish data ownership and stewardship programs
Case Study: Microsoft’s Oversharing Controls
Microsoft implemented comprehensive oversharing controls for its Copilot deployment:
Technical Implementation:
- Deployed Restricted SharePoint Search across 500,000+ sites
- Implemented encryption-based sensitivity labels for confidential content
- Configured automated permission reviews for 50,000+ security groups
- Established continuous monitoring for external sharing activities
Governance Framework:
- Created data stewardship roles with clear accountability
- Implemented quarterly access certification processes
- Deployed automated remediation for policy violations
- Established escalation procedures for sensitive data exposure
Results:
- 60% reduction in overshared content within 6 months
- 99.5% accuracy in automated permission right-sizing
- Zero unauthorized data access incidents during Copilot rollout
- Comprehensive audit trails supporting regulatory compliance
The implementation ensured Copilot could only access appropriately shared content while maintaining productivity and collaboration benefits.
🔗 See how audit logs support this
4. Train Users and Enforce AI Usage Policies
Comprehensive Training and Policy Framework:
Structured Training Program Development:
- Create role-specific Copilot training modules tailored to job functions
- Develop interactive scenarios demonstrating appropriate and inappropriate usage
- Implement mandatory completion requirements with progress tracking
- Establish continuous learning pathways through Microsoft Viva Learning
- Create assessment mechanisms to validate user understanding
AI Usage Policy Creation:
- Develop clear guidelines for acceptable Copilot interactions
- Establish protocols for handling sensitive information in prompts
- Create escalation procedures for potential policy violations
- Define consequences for policy non-compliance
- Implement regular policy review and update processes
Advanced Monitoring and Compliance:
- Deploy Microsoft Purview Communication Compliance for prompt monitoring
- Configure audit logs for comprehensive Copilot interaction tracking
- Implement real-time alerting for policy violations
- Establish review workflows for flagged interactions
- Create compliance reporting for management and regulatory purposes
User Feedback and Continuous Improvement:
- Implement feedback collection mechanisms through Microsoft Forms
- Establish user champion networks for peer-to-peer support
- Configure usage analytics dashboards for adoption monitoring
- Create regular pulse surveys to measure user satisfaction
- Develop improvement recommendations based on usage patterns
Case Study: British Columbia Investment Management Corp (BCI)
BCI implemented a comprehensive training and governance program for their Copilot deployment:
Training Implementation:
- Developed role-specific training modules for 2,000+ employees
- Created interactive workshops focusing on prompt safety and compliance
- Implemented mandatory certification requirements before Copilot access
- Established ongoing education through lunch-and-learn sessions
Policy Framework:
- Created comprehensive AI usage policies aligned with financial regulations
- Implemented real-time monitoring for sensitive financial data in prompts
- Established clear escalation procedures for compliance violations
- Developed regular audit processes for policy effectiveness
Governance Results:
- Productivity Gains: 10-20% increase in productivity for 84% of Copilot users
- Time Savings: Over 2,300 person-hours saved through automation
- Audit Efficiency: 30% reduction in time spent on internal audit reports
- Compliance: Zero policy violations during 12-month implementation period
- User Satisfaction: 68% increase in job satisfaction among Copilot users
BCI’s success demonstrates that proper training and governance can deliver significant productivity benefits while maintaining strict compliance standards.
🔗 Explore enterprise Copilot case studies
5. Deploy in Phases and Continuously Improve
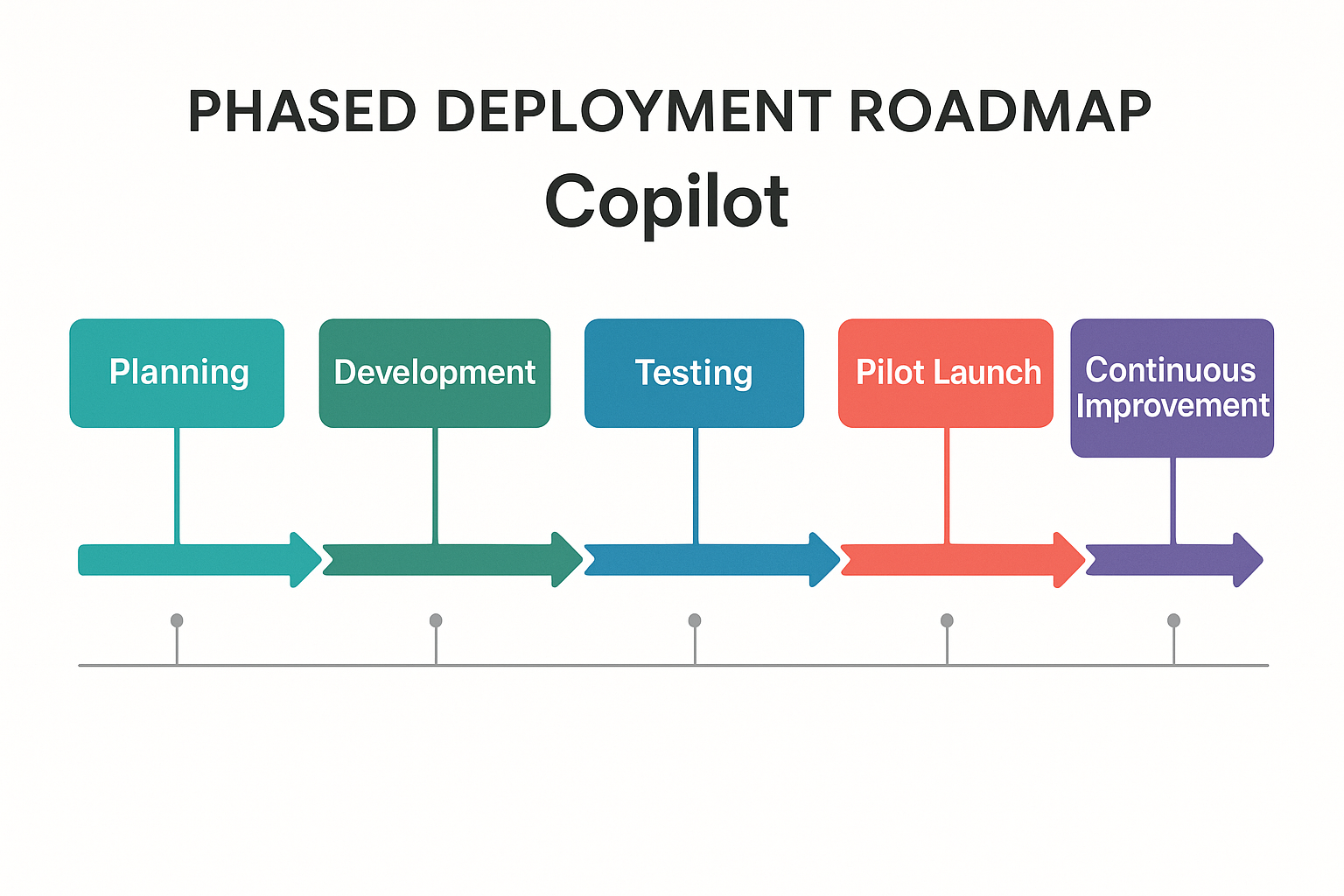
Strategic Phased Deployment Framework:
Phase 1: Foundation and Governance Setup (Months 1-2)
- Complete comprehensive infrastructure and security assessments
- Establish baseline governance policies and compliance frameworks
- Deploy Microsoft Purview data classification and DLP policies
- Conduct Microsoft Entra access audits and implement overshare scans
- Create success metrics and monitoring dashboards
- Select pilot group participants and establish success criteria
Phase 2: Controlled Pilot Implementation (Months 3-4)
- Deploy Copilot licenses to 50-100 selected pilot users
- Implement intensive training and onboarding programs
- Establish daily feedback collection and analysis processes
- Monitor usage patterns and identify optimization opportunities
- Validate use cases and document best practices
- Generate ROI projections and business case validation
Phase 3: Department-by-Department Expansion (Months 5-8)
- Deploy to high-value departments based on pilot learnings
- Customize training materials and use cases for specific roles
- Train department champions and establish peer support networks
- Implement advanced monitoring and compliance controls
- Iterate policies based on real-world usage patterns
- Document success stories and create reference implementations
Phase 4: Enterprise-Wide Deployment (Months 9-12)
- Complete organization-wide Copilot rollout
- Launch self-service resources and automated support systems
- Establish Center of Excellence (CoE) for ongoing governance
- Implement automated monitoring and compliance systems
- Plan advanced feature adoption and integration strategies
- Create innovation roadmap for future AI capabilities
Advanced Monitoring and Analytics:
- Use Microsoft 365 admin center for license management and feature controls
- Deploy Power BI dashboards for real-time usage analytics and ROI tracking
- Configure Microsoft Purview for comprehensive audit and compliance monitoring
- Implement user adoption scoring and engagement metrics
- Establish automated alerting for usage anomalies and policy violations
Continuous Improvement Framework:
- Conduct monthly usage reviews and policy optimization sessions
- Track productivity metrics and business outcome achievement
- Monitor Microsoft 365 roadmap for new features and capabilities
- Implement regular user satisfaction surveys and feedback integration
- Establish quarterly business reviews with stakeholder alignment
- Create knowledge sharing platforms for organizational learning
Case Study: Microsoft’s Four-Phase Enterprise Rollout
Microsoft’s internal deployment demonstrates the effectiveness of a structured phased approach:
Phase Zero – Engineering Team Validation:
- Provided early access to Copilot engineering teams
- Conducted extensive testing from insider technical perspectives
- Validated core functionality and identified optimization opportunities
Phase One – Limited On-Demand Licensing:
- Issued controlled licenses for key business scenarios
- Gathered validation data for critical use cases
- Established feedback loops for product improvement
Phase Two – Support Team Extension:
- Extended licenses to teams requiring Copilot understanding for support
- Included legal, security, and compliance teams in validation process
- Obtained necessary approvals and risk assessments
Phase Three – Enterprise Deployment:
- Deployed to all 300,000+ Microsoft employees and external staff
- Implemented comprehensive governance and monitoring systems
- Achieved full organizational adoption with maintained security posture
Key Success Factors:
- Structured Accountability: Clear phase gates and success criteria
- IT Administrative Control: Granular feature and access management
- Comprehensive Training: Role-specific education and support resources
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time usage analytics and compliance tracking
- Iterative Improvement: Regular policy refinement based on usage patterns
The phased approach enabled Microsoft to validate value, optimize implementation, and scale safely across a massive organization while maintaining security and compliance standards.
🔗 Read the full deployment strategy
Copilot Security Conclusion
This comprehensive framework provides organizations with the essential knowledge and practical steps needed to deploy Microsoft Copilot securely and effectively.
By implementing these five best practices:
- Zero Trust architecture
- Comprehensive data protection
- Permission auditing
- User training
- Phased deployment
organizations can harness the productivity benefits of AI while maintaining robust security and compliance postures.
The real-world case studies from Microsoft, BCI, and its internal modeling demonstrate that with proper planning, governance, and execution, organizations can achieve significant productivity gains while meeting the most stringent security and regulatory requirements.
Success requires commitment to structured implementation, continuous monitoring, and iterative improvement based on actual usage patterns and business outcomes.
Need help with your Copilot implementation planning?
Cloud Revolution helps organizations unlock the full potential of Microsoft Teams and Copilot—guiding you from planning through adoption with seamless, outcome-driven solutions.
As Microsoft Partner of the Year 2023 and a finalist in 2022 and 2024, we’re trusted worldwide to simplify collaboration and maximize ROI.
👉 Book a free consultation to see how we can help.
Is Your Organization Ready
for Microsoft 365 Copilot?
In just 2 minutes, you’ll discover how prepared your organization
is to unlock the power of Microsoft 365 Copilot.